AI Assistant Guide¶
Notolog includes an AI-powered assistant that supports multiple backends for text generation and assistance.
Table of Contents¶
- Overview
- Supported Backends
- OpenAI API Setup
- On-Device LLM (ONNX)
- Module llama.cpp (GGUF)
- Using the AI Assistant
- Best Practices
- Troubleshooting
Overview¶
The AI Assistant provides:
- Chat-style interface for natural conversations
- Context-aware responses with prompt history
- Multiple backends for flexibility
- Privacy options with local LLM support
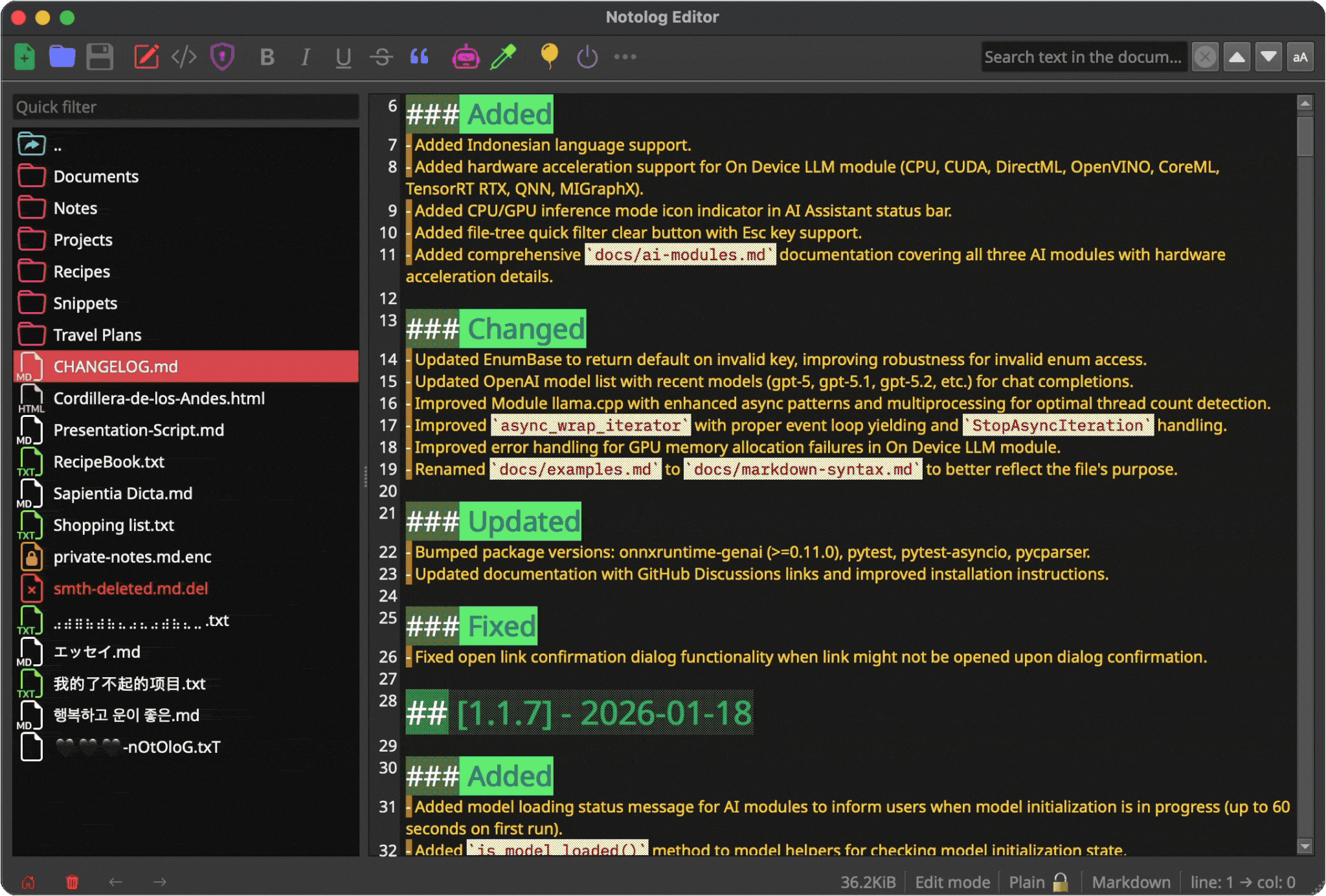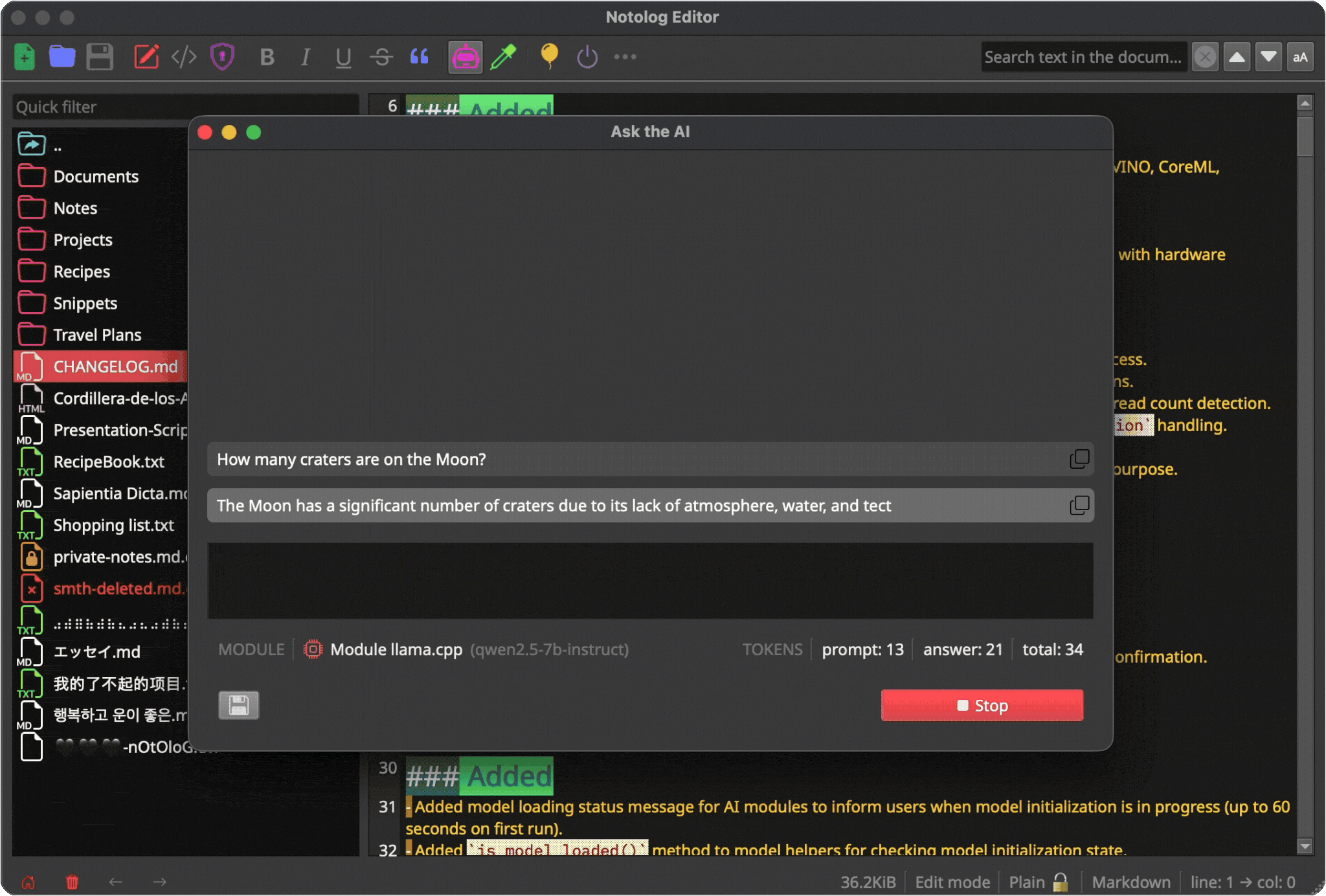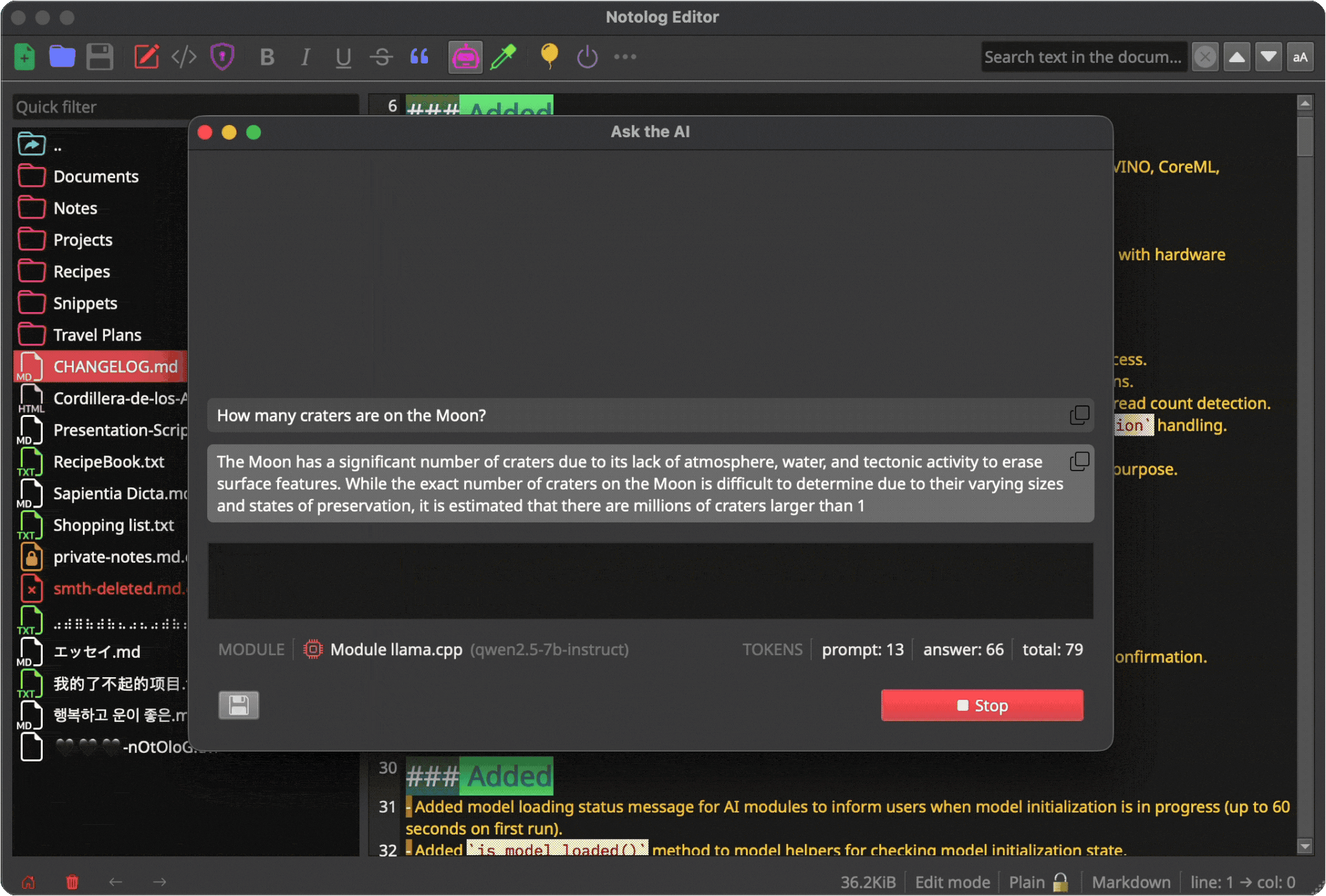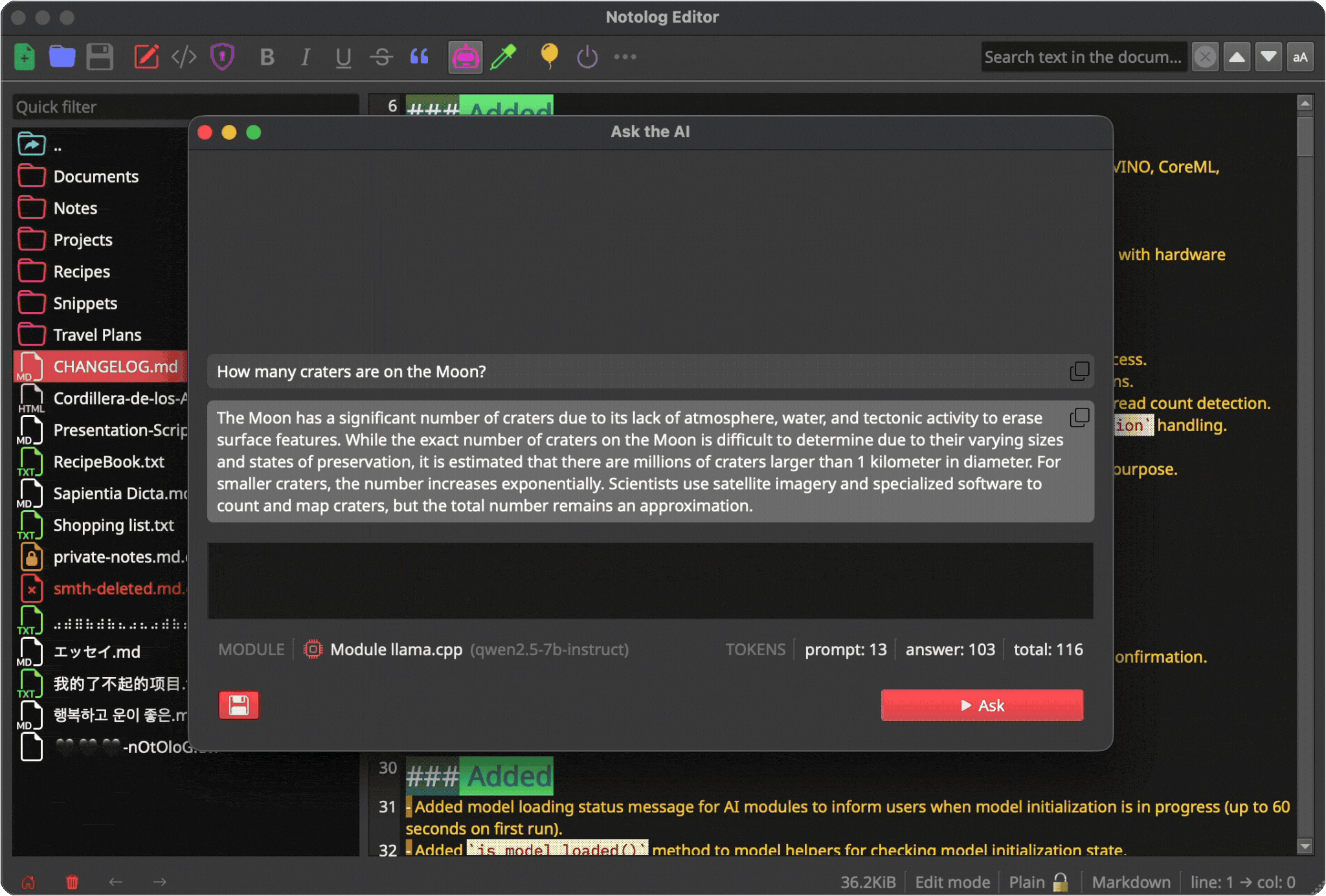
Access via: Tools → AI Assistant
Supported Backends¶
| Backend | Model Format | Requirements | Privacy |
|---|---|---|---|
| OpenAI API | Cloud-based | API key, internet | Cloud processed |
| On-Device LLM | ONNX | 8GB+ RAM | Fully local |
| Module llama.cpp | GGUF | 8GB+ RAM, C++ compiler | Fully local |
OpenAI API Setup¶
Requirements¶
- OpenAI API account
- Valid API key
- Internet connection
Configuration¶
- Go to
Settings→OpenAI APItab - Enter your API URL (default: OpenAI endpoint)
- Enter your API key in the secure field
- Configure optional settings:
| Setting | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| API URL | API endpoint URL | https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions |
| API Key | Your OpenAI API key (stored encrypted) | (required) |
| Supported Models | GPT model to use | gpt-5.2 |
| System Prompt | Initial context/instructions | (empty) |
| Temperature | Response creativity (0-100 → 0.0-1.0) | 20 (0.2) |
| Maximum Response Tokens | Maximum response length (0 = unlimited) | 0 |
| Prompt History Size | Number of turns to remember | 0 |
Security Notes¶
- API keys are stored encrypted locally
- Keys are never transmitted except to OpenAI
- Consider using environment variables for added security
On-Device LLM (ONNX)¶
Run AI models locally using ONNX Runtime GenAI.
Requirements¶
- Python 3.10-3.13 (ONNX GenAI limitation)
- 8GB+ RAM (16GB recommended)
- ONNX format model files
Supported Models¶
Download ONNX-optimized models from: - Hugging Face ONNX models - Microsoft's Phi models (recommended for efficiency)
Configuration¶
- Go to
Settings→On Device LLMtab - Set ONNX Model Location to your ONNX model directory
- Configure generation parameters:
| Setting | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| ONNX Model Location | Path to ONNX model directory | (required) |
| Temperature | Response randomness (0-100 → 0.0-1.0) | 20 (0.2) |
| Maximum Response Tokens | Maximum response length (0 = unlimited) | 0 |
| Prompt History Size | Number of turns to remember | 0 |
First Run Notice¶
Model Loading Time
On first use, ONNX models may take up to 60 seconds to load. The application will display a loading message. Subsequent uses are faster due to caching.
Model Directory Structure¶
Your ONNX model directory should contain:
model_directory/
├── model.onnx # Main model file
├── model.onnx.data # Model weights (if separate)
├── tokenizer.json # Tokenizer configuration
└── config.json # Model configuration
Module llama.cpp (GGUF)¶
Run GGUF-format models using llama.cpp bindings.
Requirements¶
llama-cpp-pythonpackage- C++ compiler (for installation)
- 8GB+ RAM
- GGUF model file
Installation¶
# Option 1: Install with Notolog extras
pip install "notolog[llama]"
# Option 2: Install separately
pip install llama-cpp-python
# Linux users may need:
sudo apt-get install build-essential
Supported Models¶
GGUF models from: - Hugging Face GGUF Models - TheBloke's Collection (historic archive, 2,000+ models)
Recommended quantizations: - Q4_K_M - Good balance of size/quality - Q5_K_M - Better quality, larger size - Q8_0 - Near-original quality
Configuration¶
- Go to
Settings→Module llama.cpptab - Set Model Location to your
.gguffile - Configure parameters:
| Setting | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| Model Location | Path to .gguf model file | (required) |
| Context Window Size | Token context size (1-65536) | 2048 |
| Chat Formats | Model's chat template | auto |
| System Prompt | Initial instructions for the model | (empty) |
| Response Temperature | Response randomness (0-100 → 0.0-1.0) | 20 (0.2) |
| Max Tokens per Response | Maximum response length (0 = unlimited) | 0 |
| Size of the Prompt History | Number of turns to remember | 0 |
Chat Formats¶
Select based on your model: * chatml - Most common format * llama-2 - Meta's Llama 2 models * gemma - Google's Gemma models * mistral - Mistral AI models
Using the AI Assistant¶
Basic Workflow¶
- Open AI Assistant
- Select your preferred backend in Settings
- Type your prompt in the input field
- Press
Enteror click Send - Wait for the response
Multi-line Prompts¶
For longer prompts: * Use Ctrl+Enter for new lines * Press Enter to send
Prompt Tips¶
Be Specific:
Provide Context:
"I'm writing a Markdown document about gardening.
Suggest 5 section headers for a beginner's guide."
Request Format:
Token Usage¶
The status area shows: - Input tokens: Your prompt size - Output tokens: Response size - Total tokens: Combined usage
Best Practices¶
For Privacy¶
- Use local models (ONNX or GGUF) for sensitive content
- Review system prompts before sending
- Clear chat history when done with sensitive topics
For Performance¶
- Start with smaller models (7B parameters)
- Use quantized models (Q4_K_M) for speed
- Increase context window only if needed
- Close other applications when using large models
For Quality¶
- Use appropriate temperature:
- Low (0.1-0.3): Factual, consistent
- Medium (0.4-0.7): Balanced
- High (0.8-1.0): Creative, varied
- Provide clear, specific prompts
- Use system prompts to set context
Troubleshooting¶
"Model not found" Error¶
Cause: Invalid model path or corrupted model files.
Solution: 1. Verify the model path in Settings 2. Check that model files exist and are complete 3. Ensure file permissions allow reading
ONNX Model Takes Too Long to Load¶
Cause: First-time model initialization.
Solution: - Wait up to 60 seconds on first run - Subsequent loads are faster - A loading message will be displayed
"Application Not Responding" During Model Load¶
Cause: Model loading blocking the UI thread (fixed in v1.1.7+).
Solution: - Update to latest Notolog version - Loading now runs in background thread
llama-cpp-python Installation Fails¶
Cause: Missing C++ compiler.
Solution:
# Ubuntu/Debian
sudo apt-get install build-essential
# Fedora
sudo dnf install gcc-c++
# macOS
xcode-select --install
Out of Memory Errors¶
Cause: Model too large for available RAM.
Solution: 1. Use smaller quantized models 2. Close other applications 3. Reduce context window size 4. Consider cloud API instead
C++ Type Conversion Warning¶
Warning: _pythonToCppCopy: Cannot copy-convert ... (NoneType) to C++
Cause: Signal passing None to C++ layer (cosmetic warning, fixed in v1.1.7+).
Impact: No functional impact; warning can be ignored.
API Reference¶
For developers extending AI functionality, see: - API Reference - Module Architecture - Creating Custom Modules
For general configuration, see Configuration Guide.